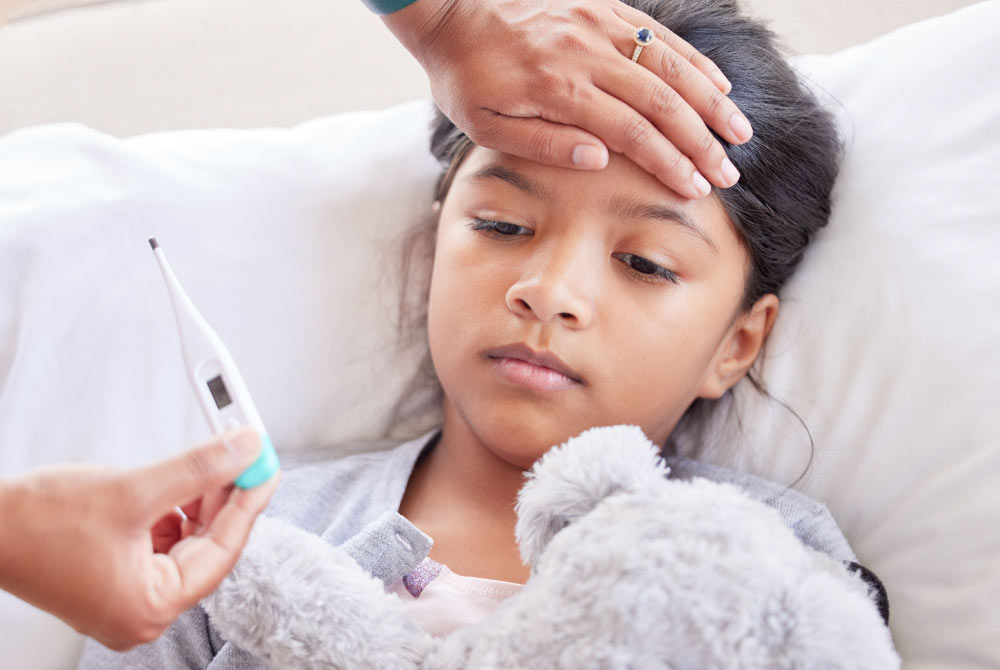
5 Things to Keep in Mind While Choosing a Pediatrician
Introduction Importance of Selecting the Right Paediatrician Choosing a pediatrician is probably one of the biggest decisions ever made by most parents. The paediatrician you will settle with will be the one who will play an important role in your c...


























































































.jpg?updatedAt=1690807054914)







































.jpg?updatedAt=1691652021648)
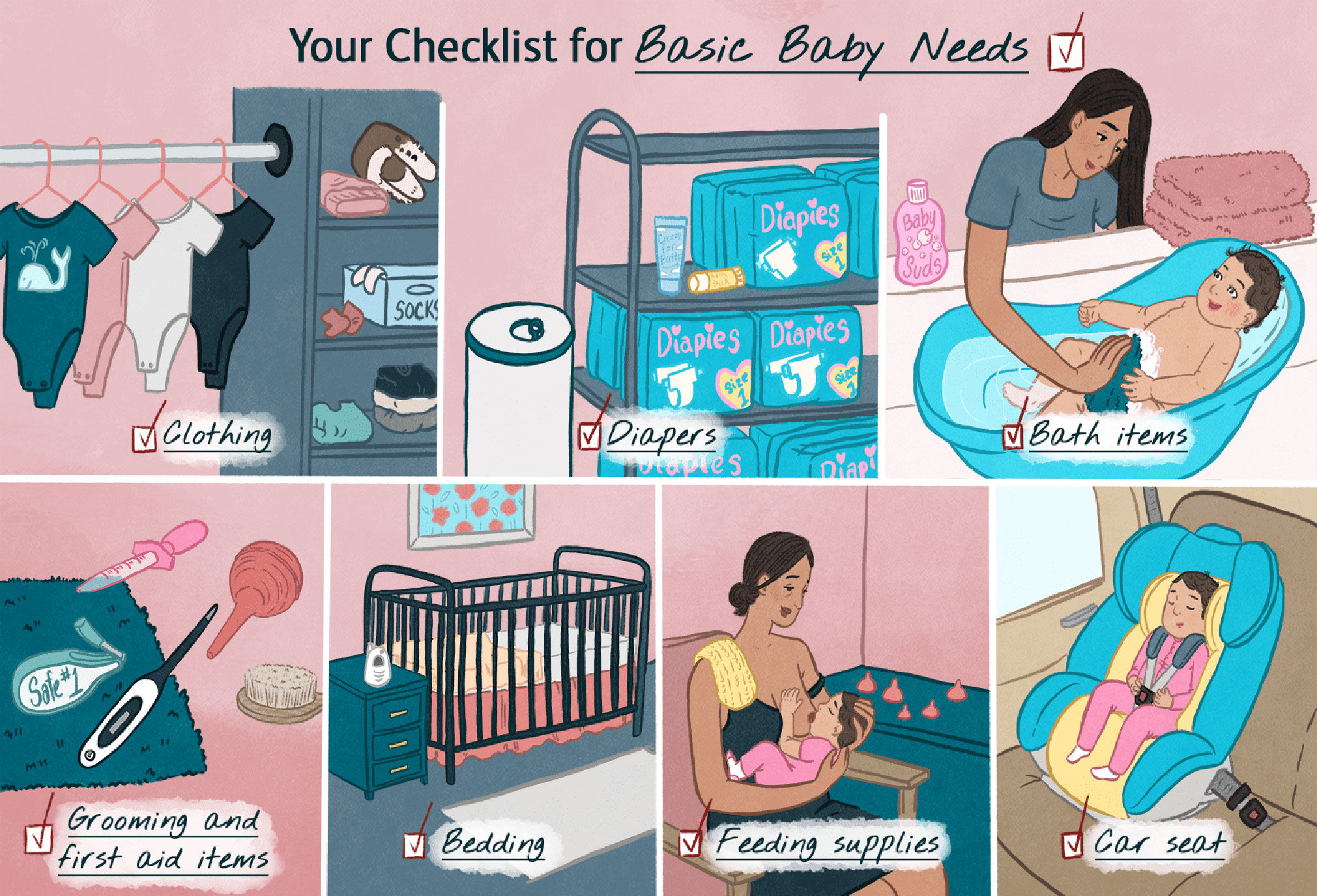


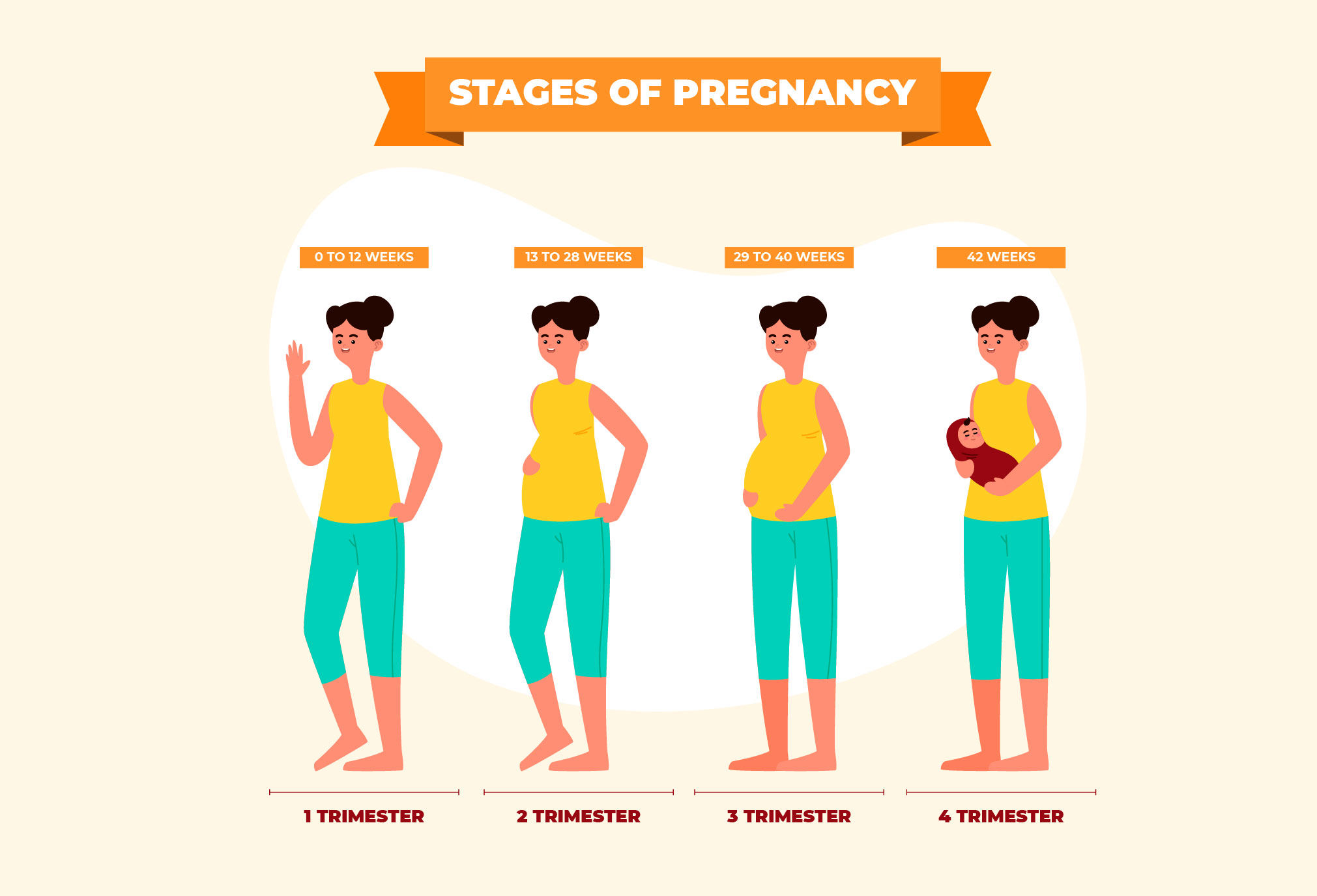




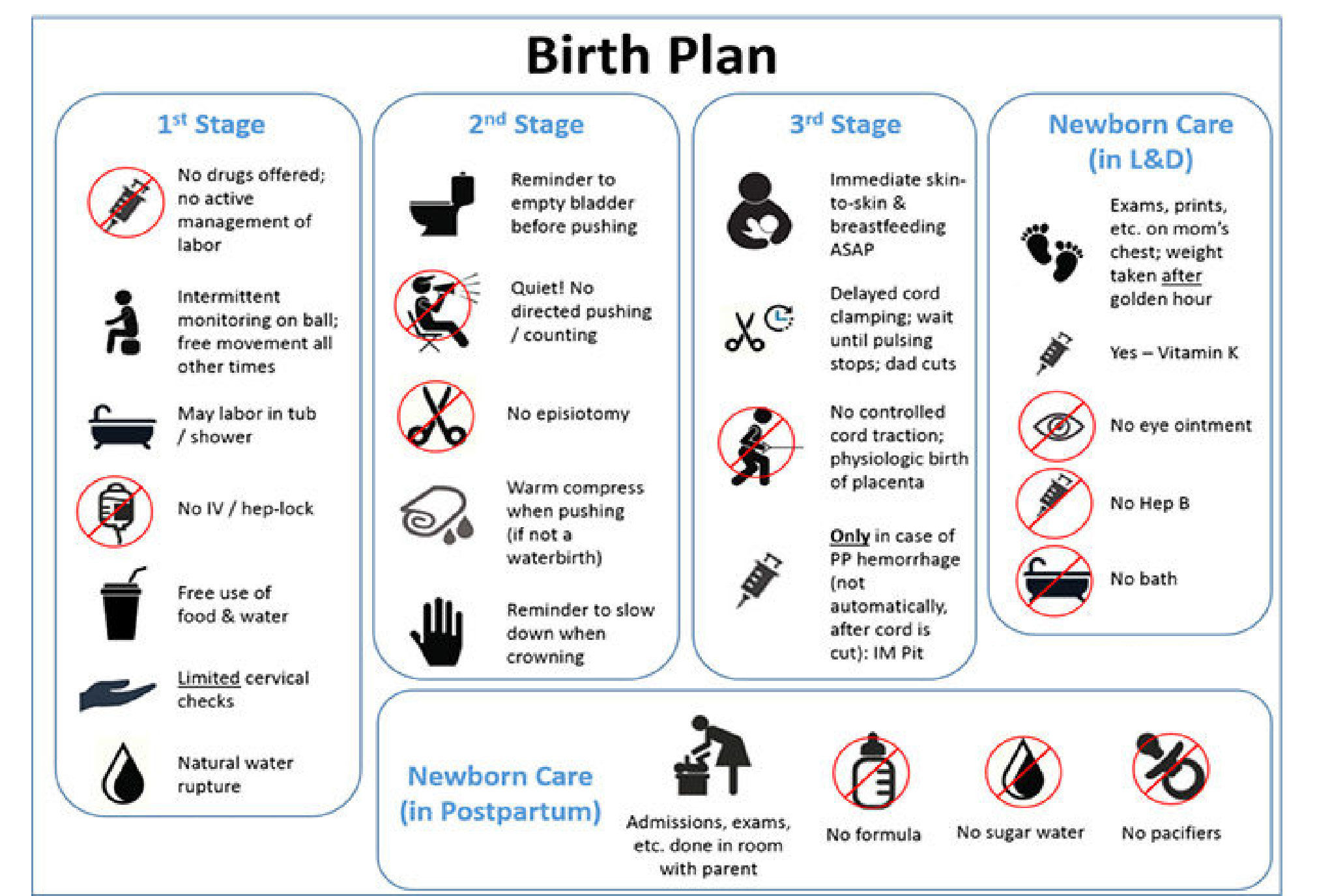
























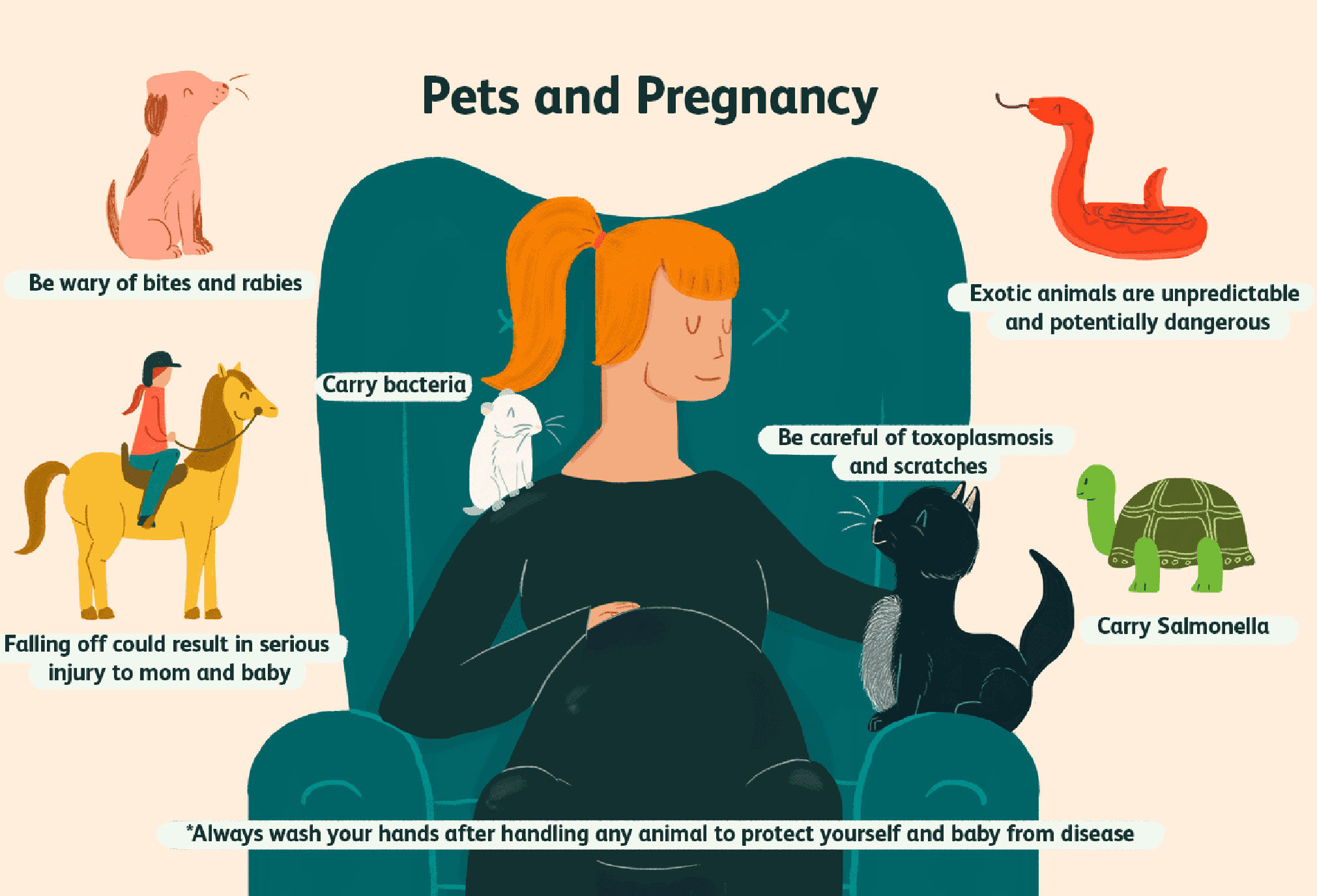








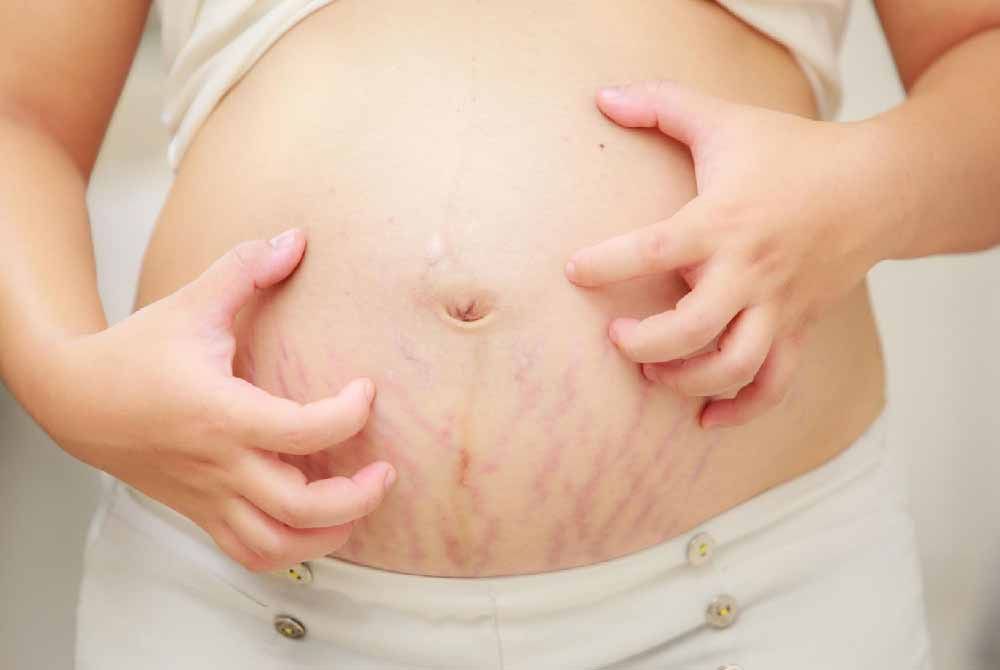



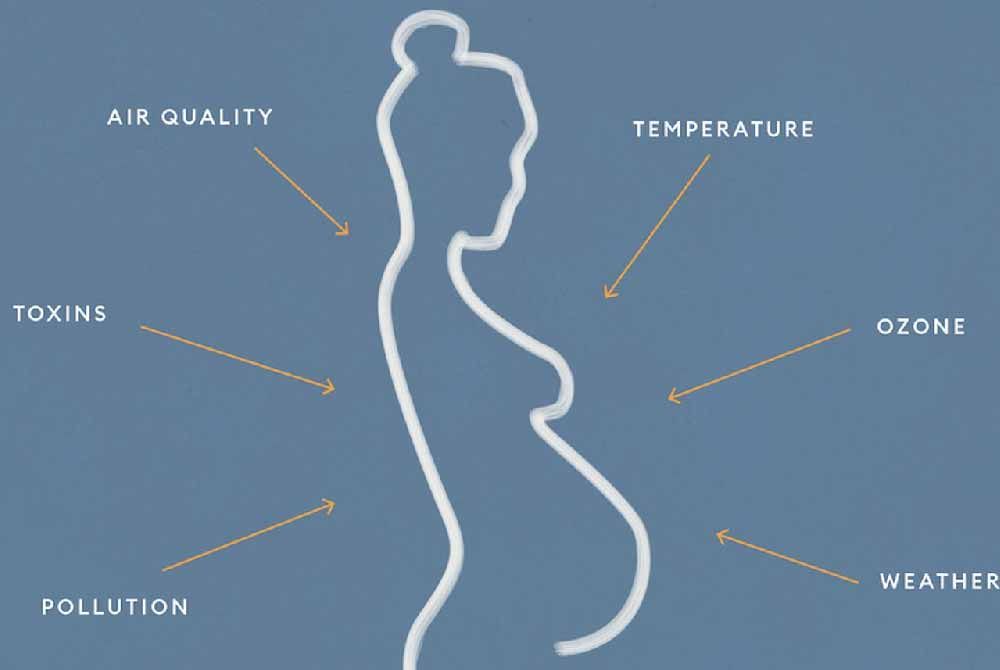





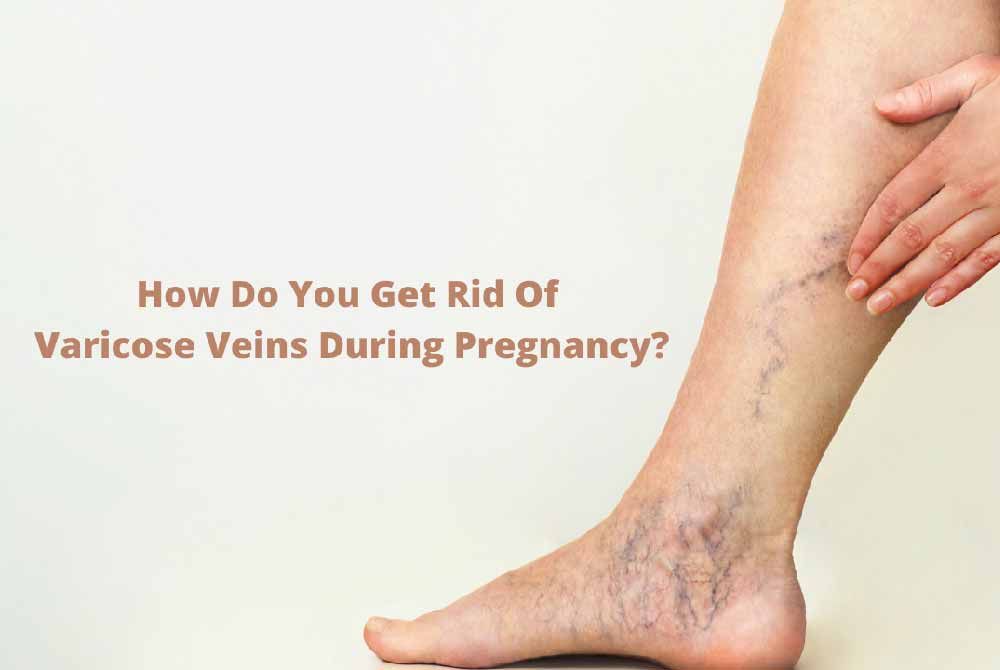















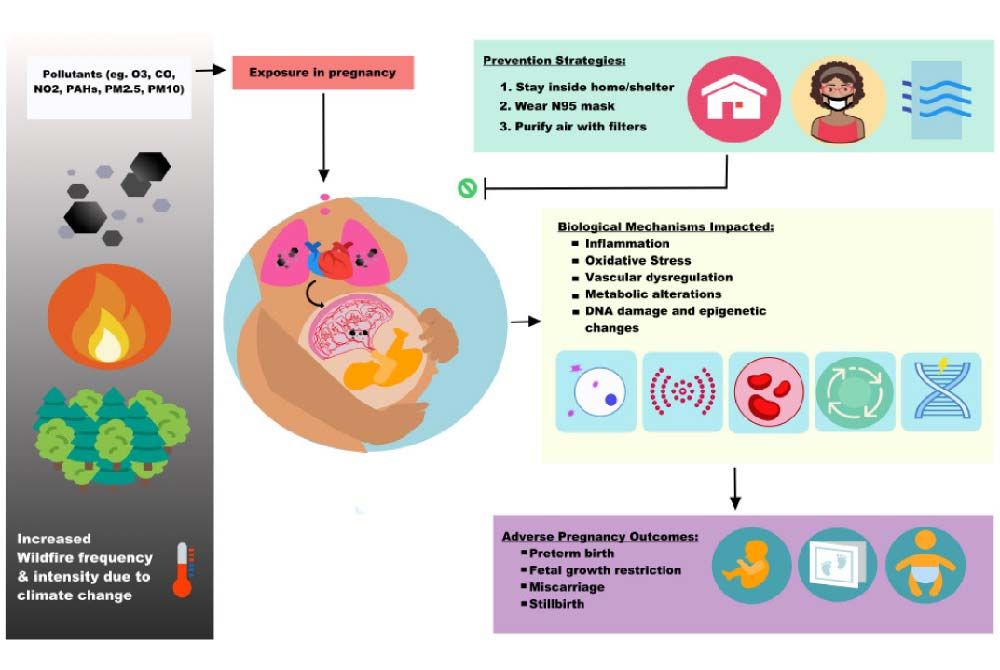


.jpg?updatedAt=1693824461461)







.jpg?updatedAt=1693825210494)



















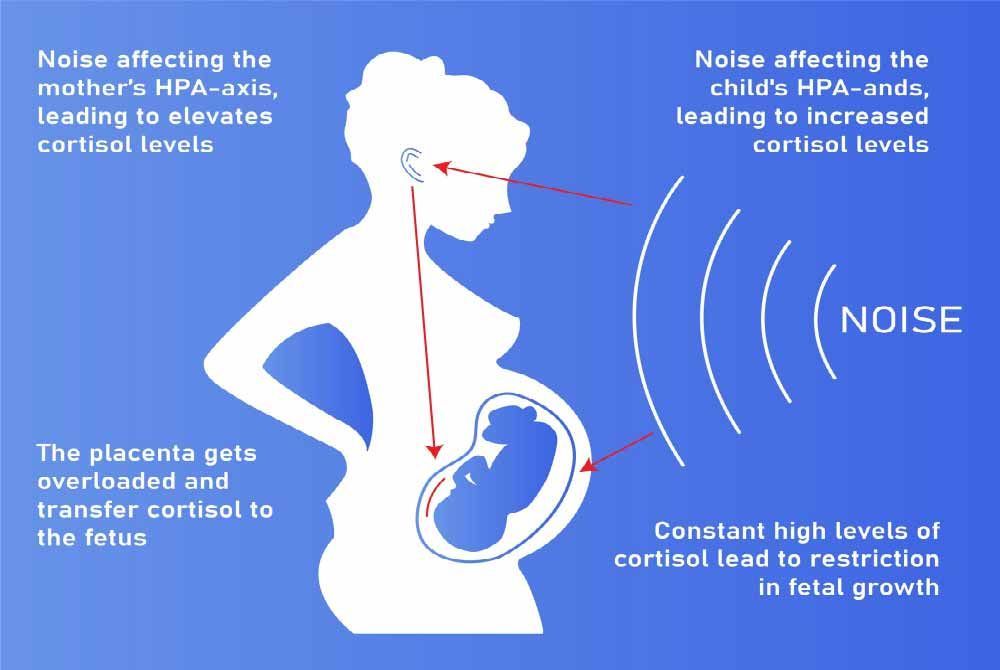
%20during%20pregnancy%20Testing%20and%20prevention-01.jpg?updatedAt=1693829505478)















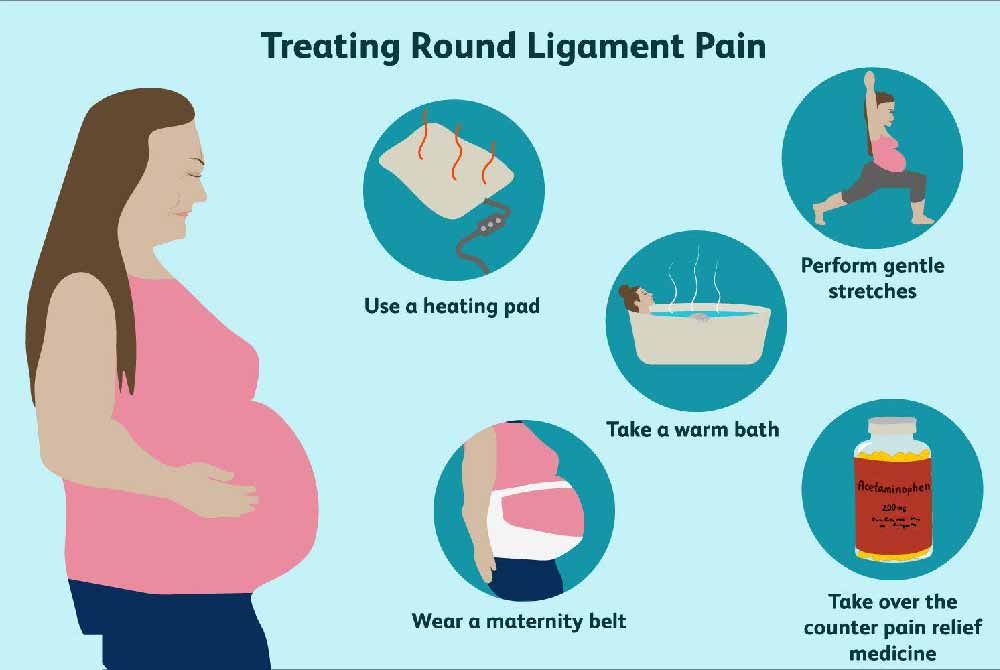


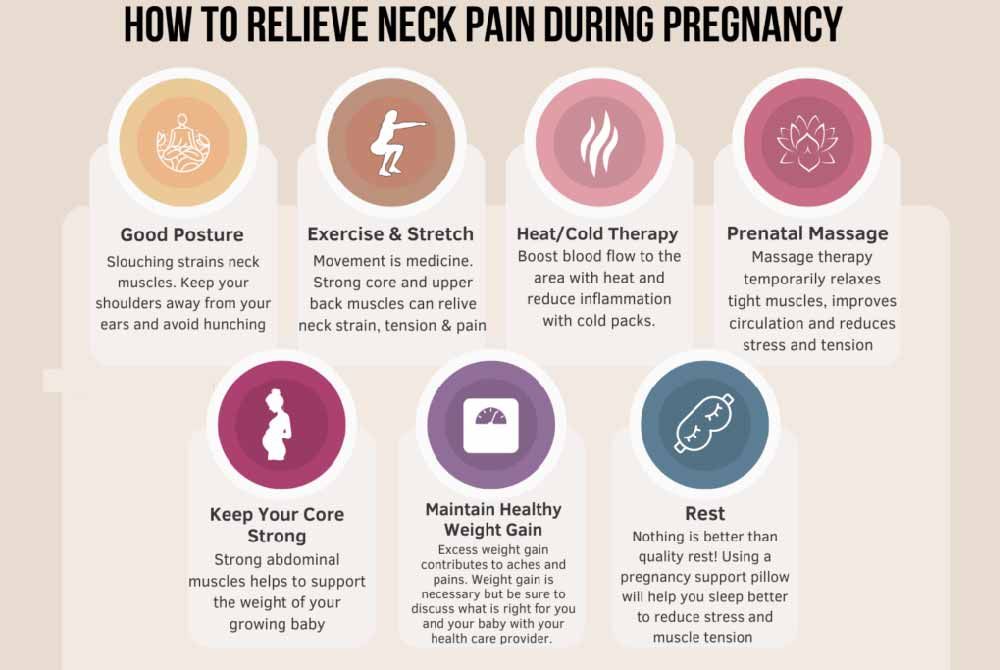


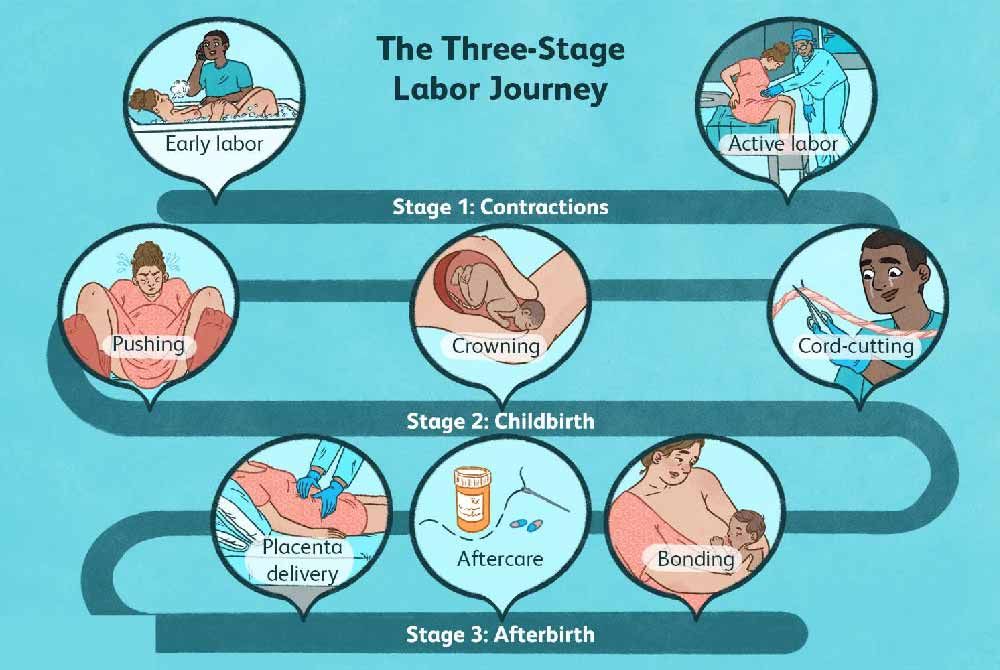
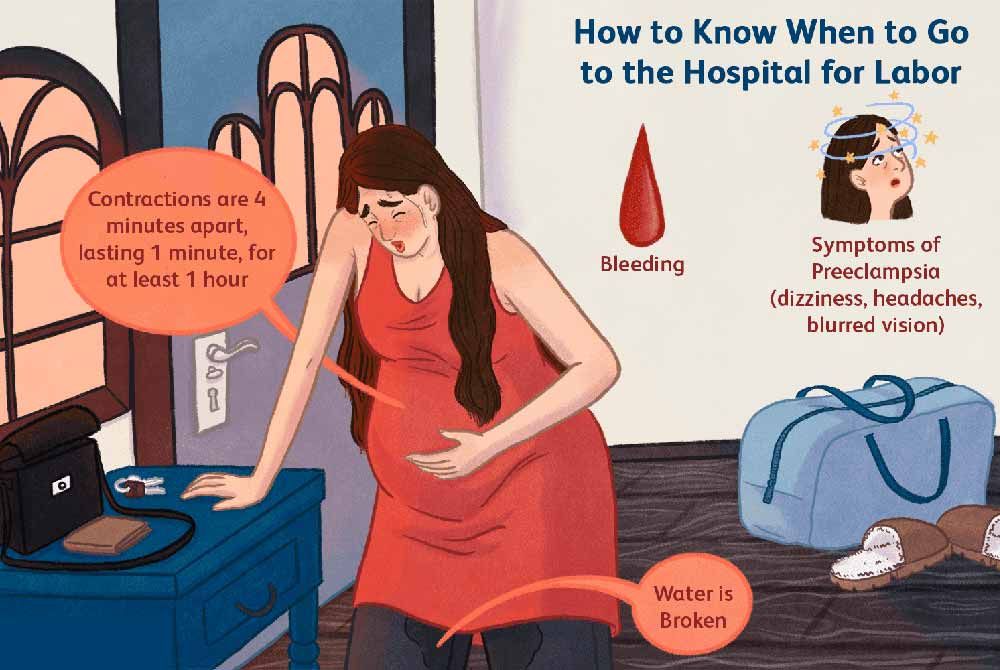
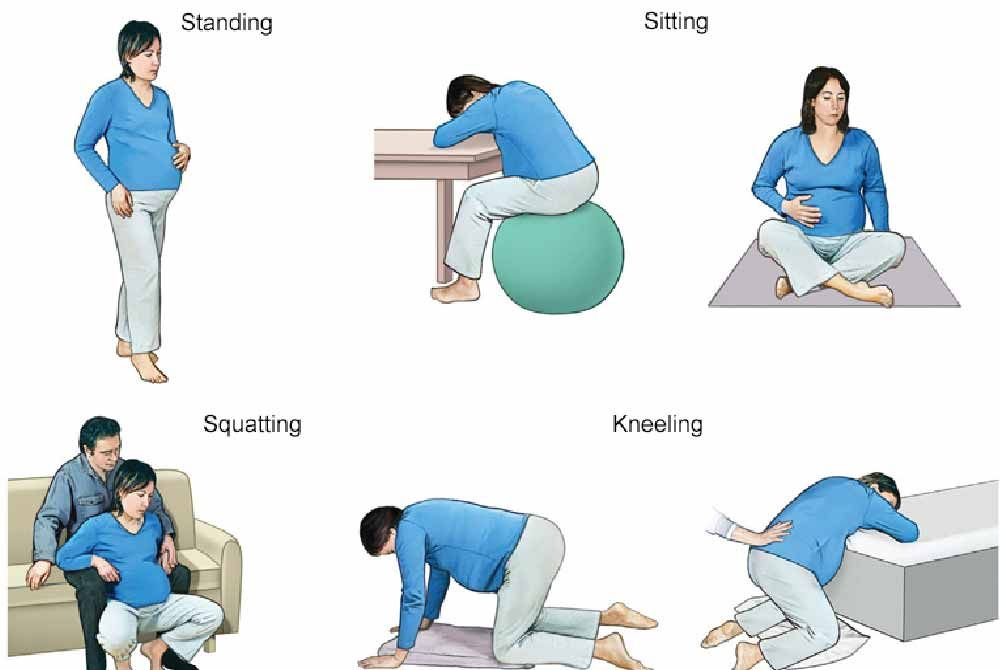
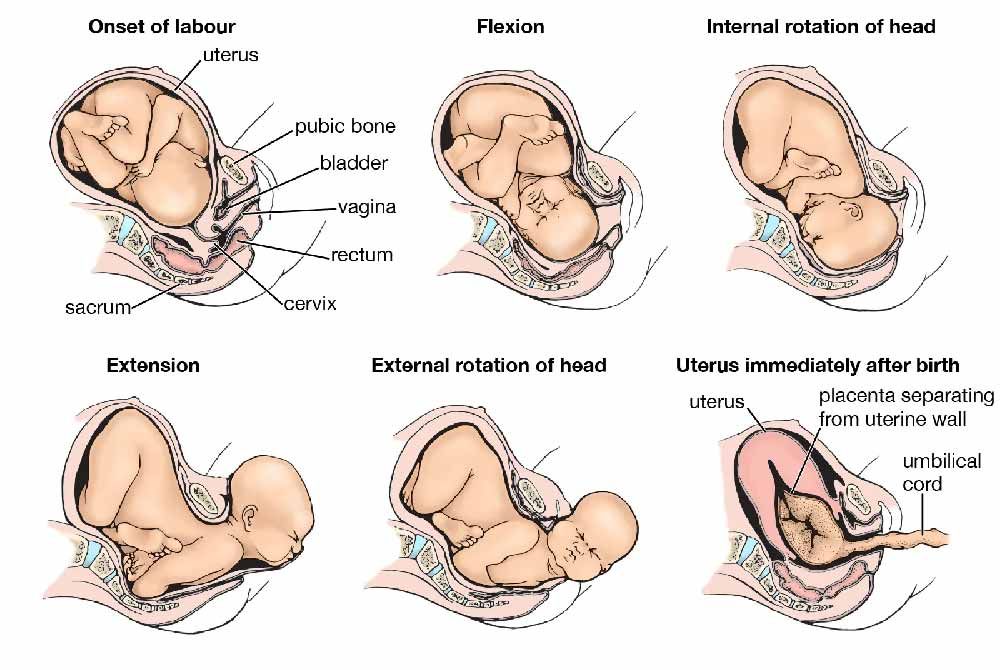

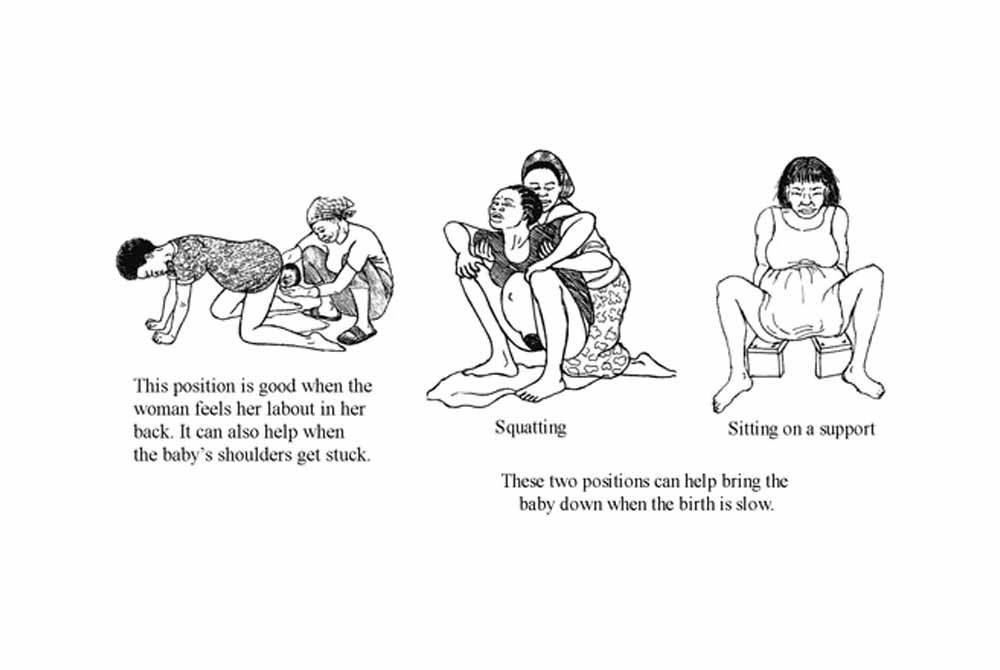

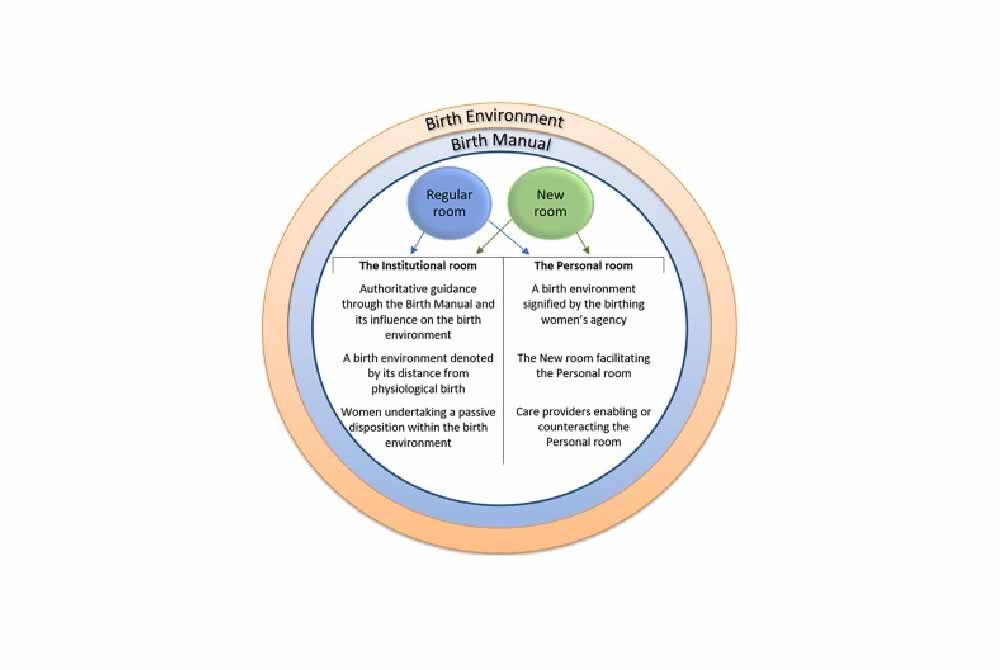
_%20Considerations%20and%20success%20factors.jpg?updatedAt=1734601999557)
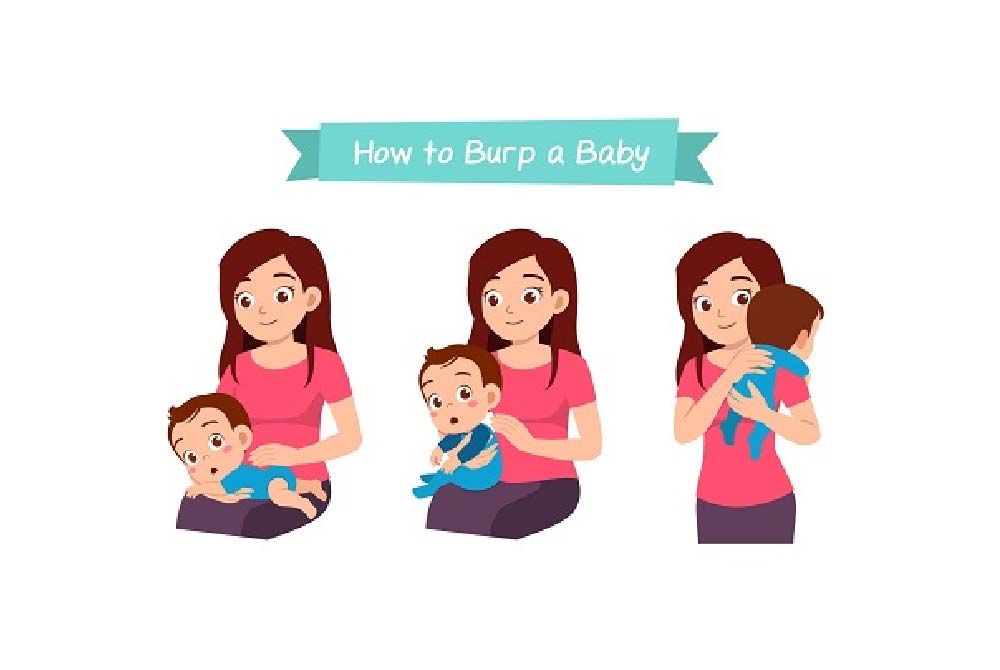



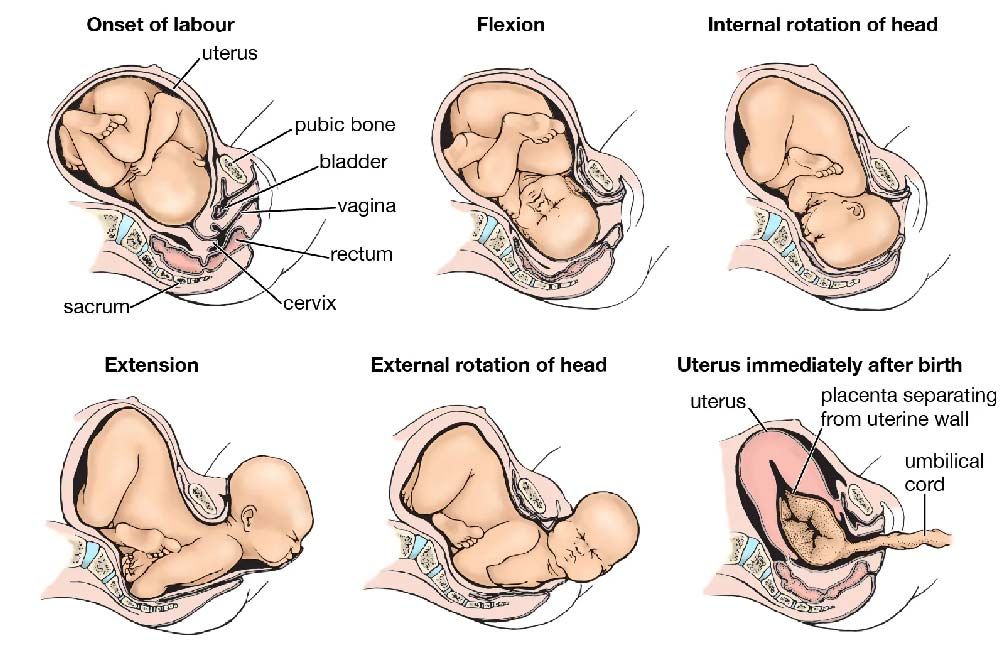






















.jpg?updatedAt=1696070546140)
.jpg?updatedAt=1696070476921)





























%20symptoms,%20including%20pain-01.jpg?updatedAt=1696332202285)











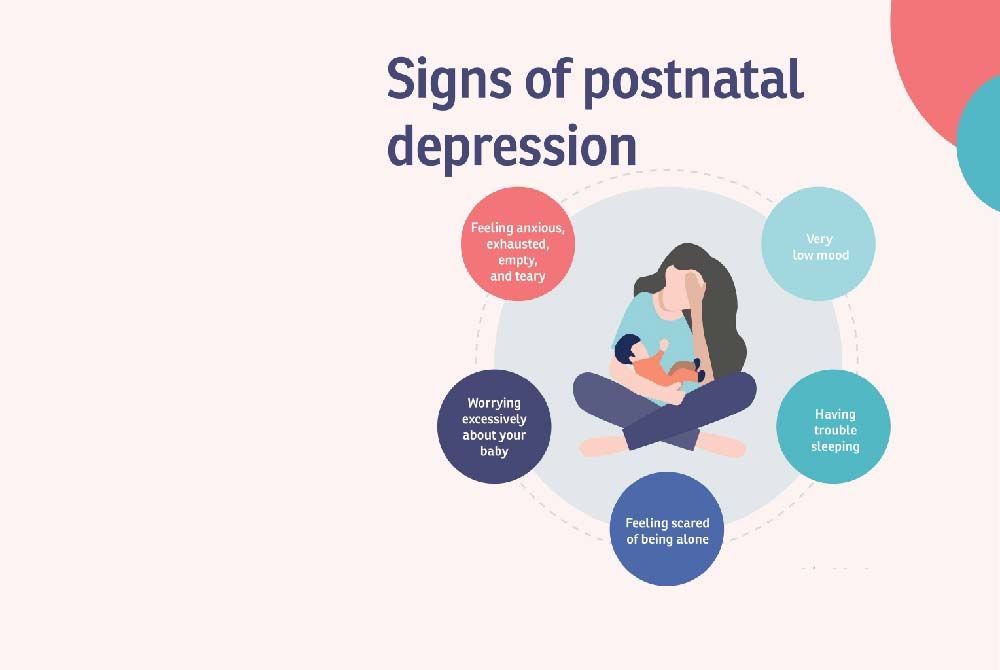




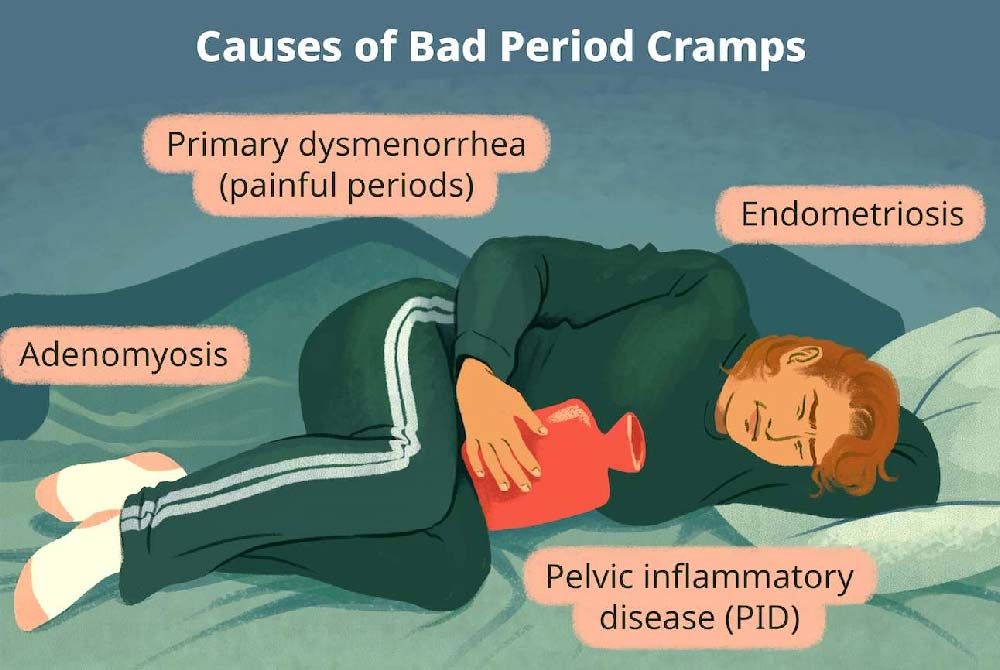

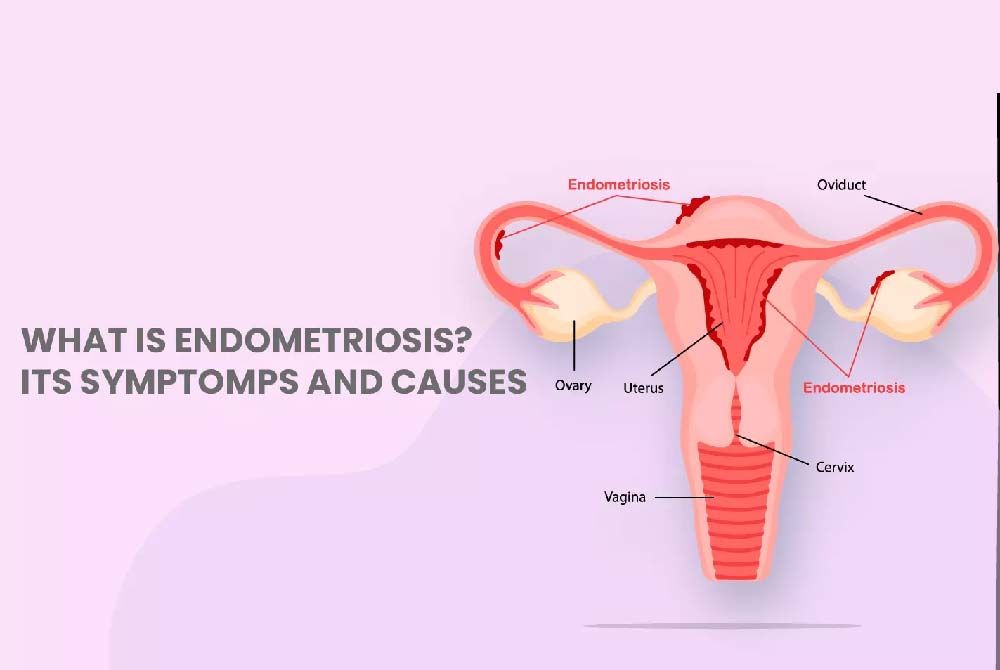










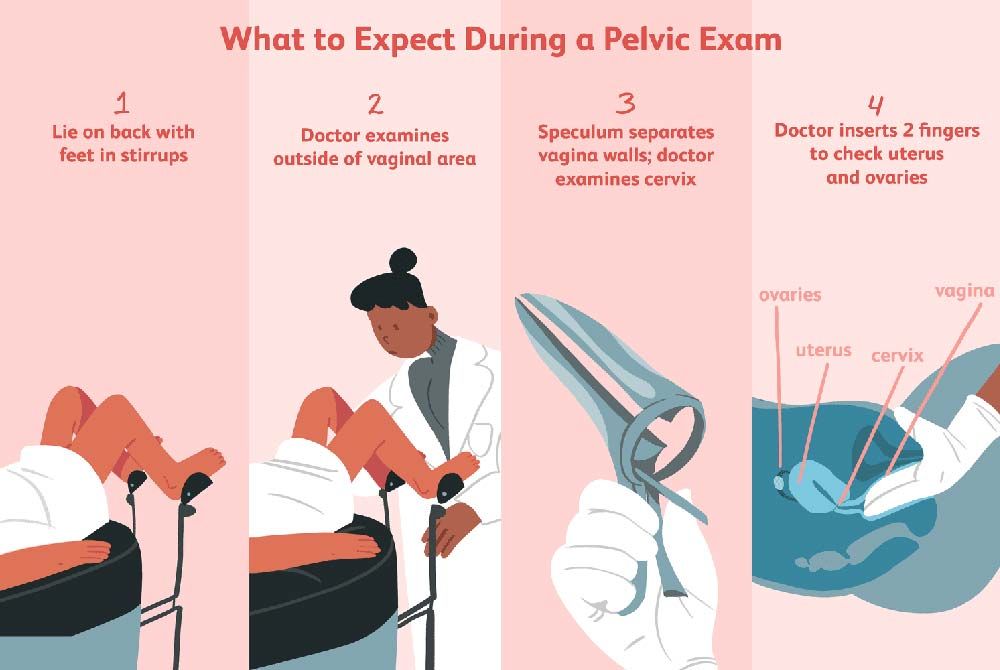
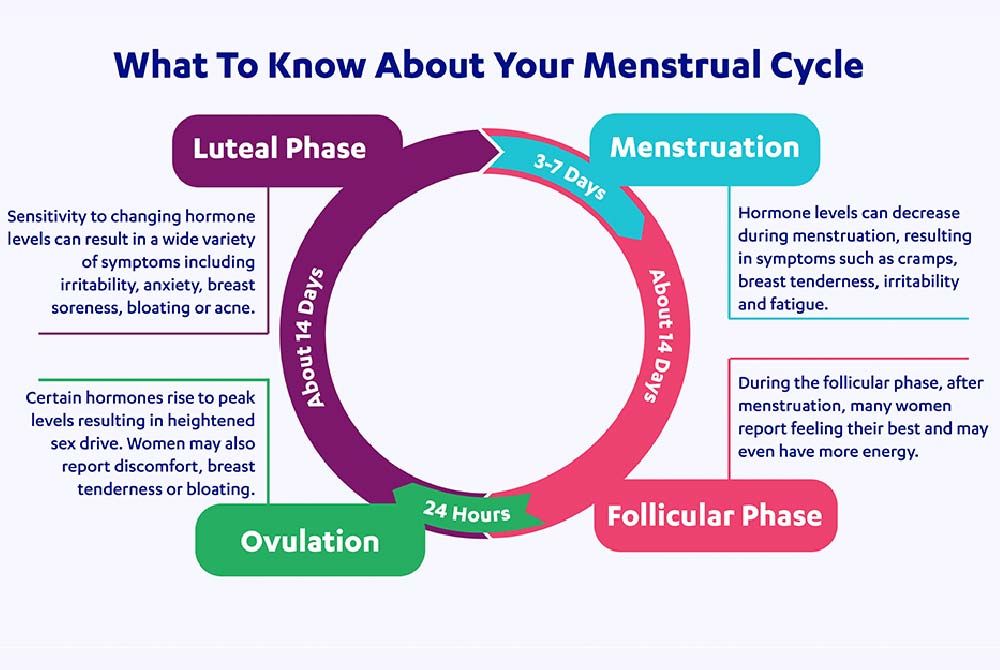
















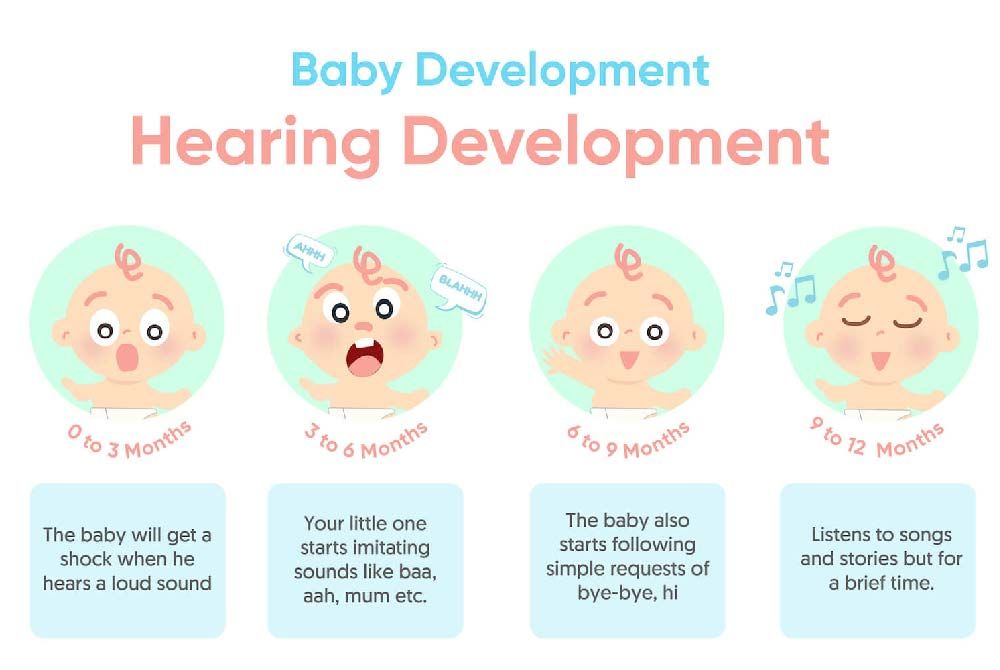
.jpg?updatedAt=1734602428063)

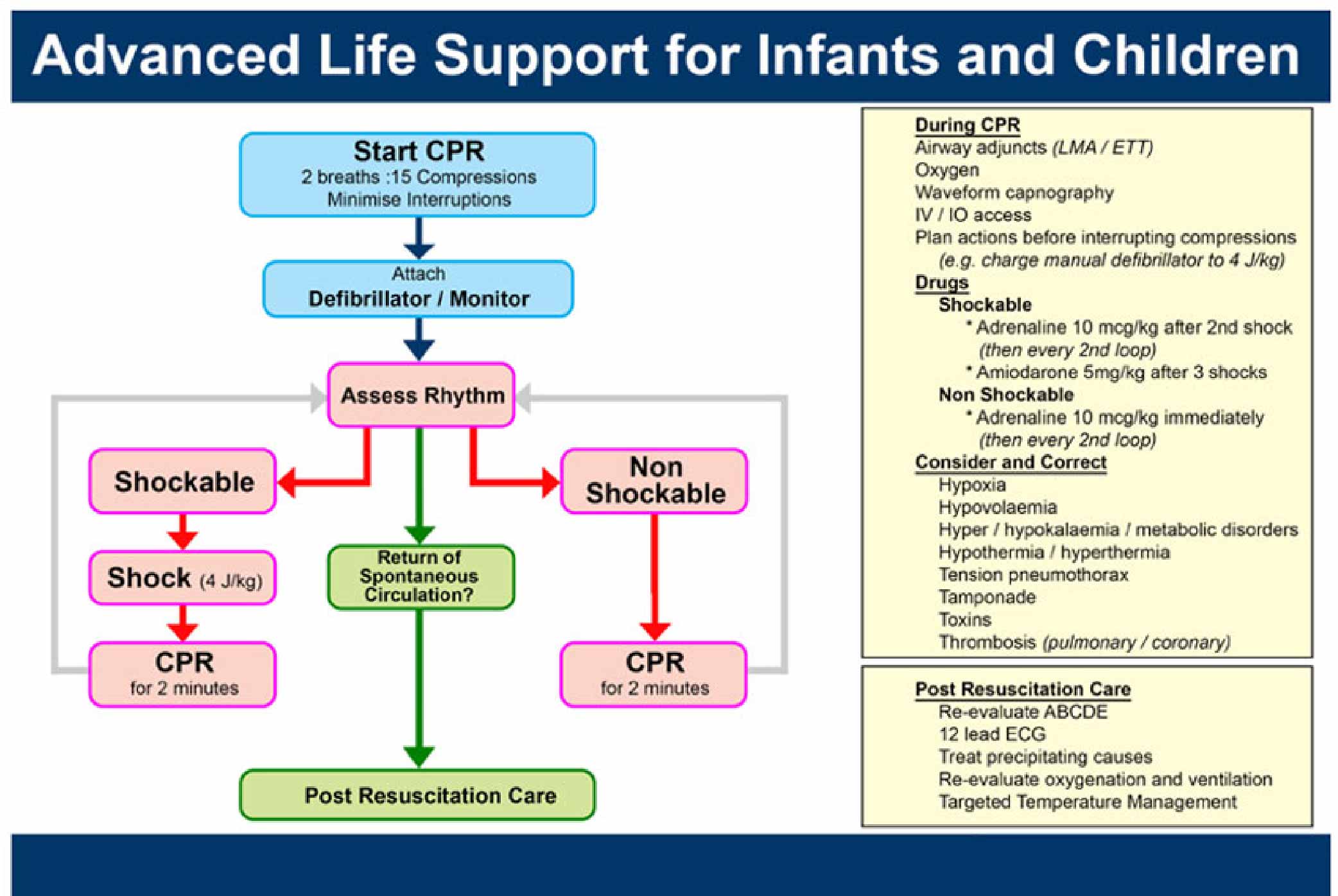
%20in%20Children-01.jpg?updatedAt=1698298638229)

.jpg?updatedAt=1698298880320)

%20in%20Preterm%20Infants.jpg?updatedAt=1734604551369)

%20Pregnancy,%20Birth%20and%20Baby-01.jpg?updatedAt=1698299202144)
















%20prevention%20and%20treatment-01.jpg?updatedAt=1698301053731)









.jpg?updatedAt=1698650657711)



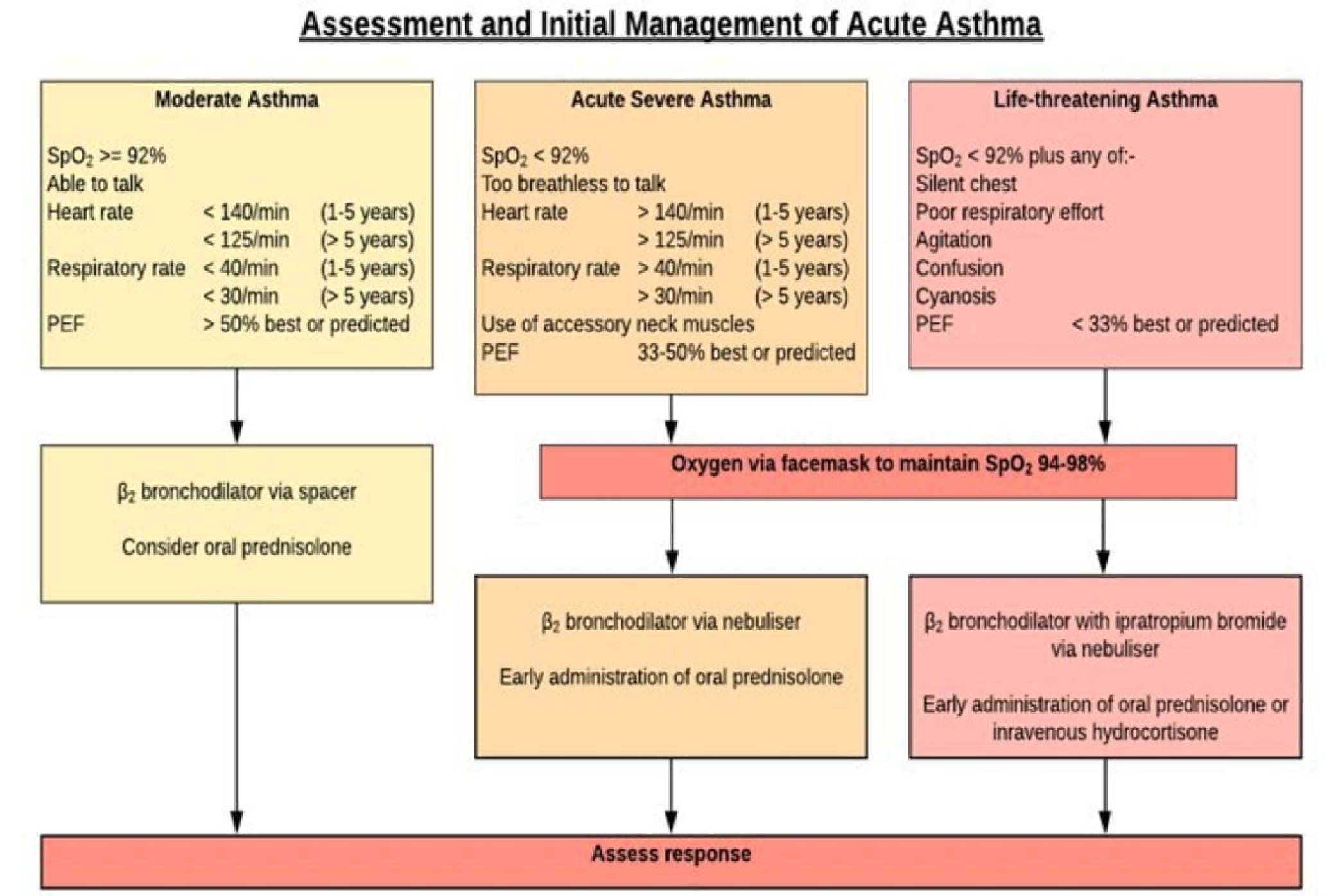
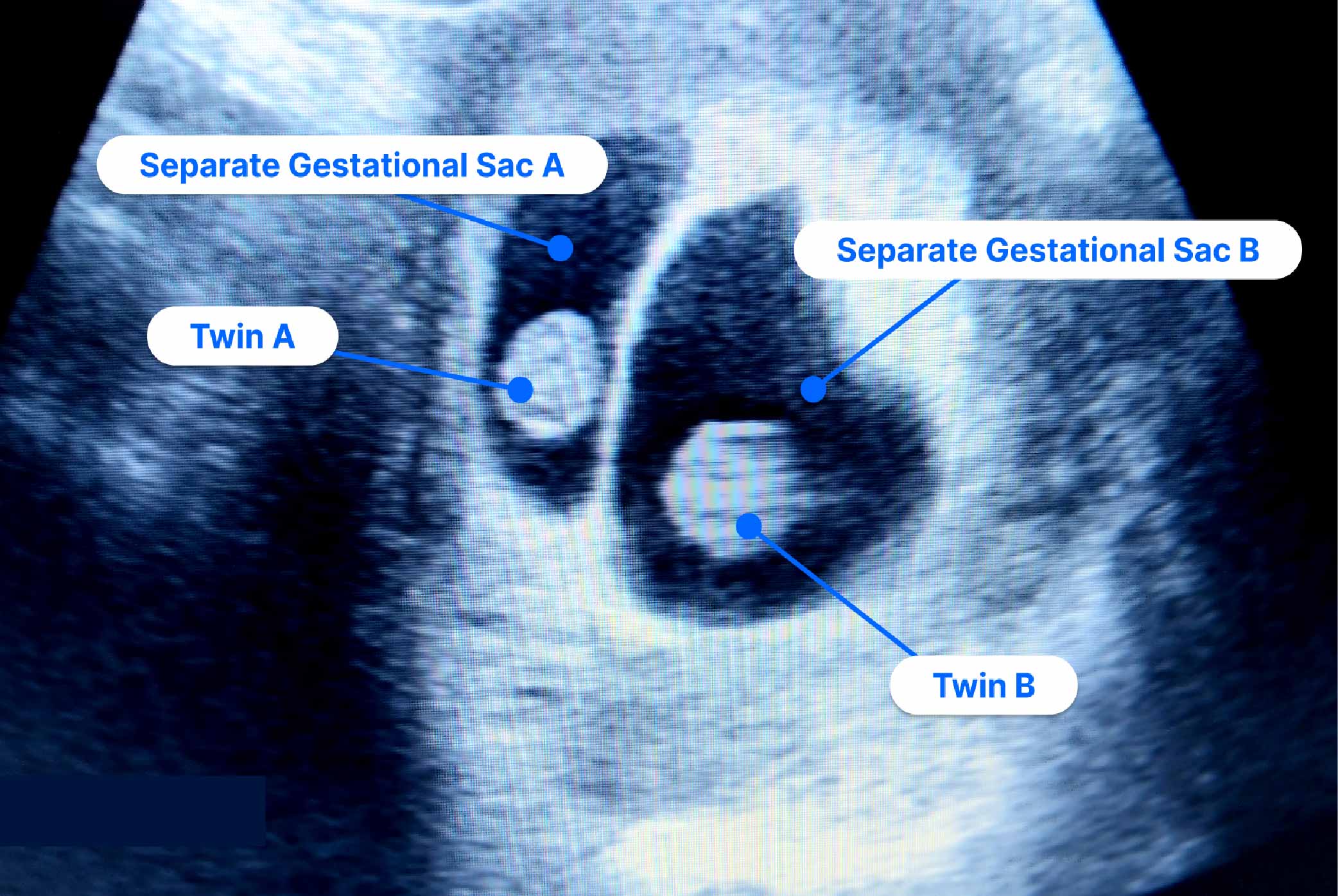









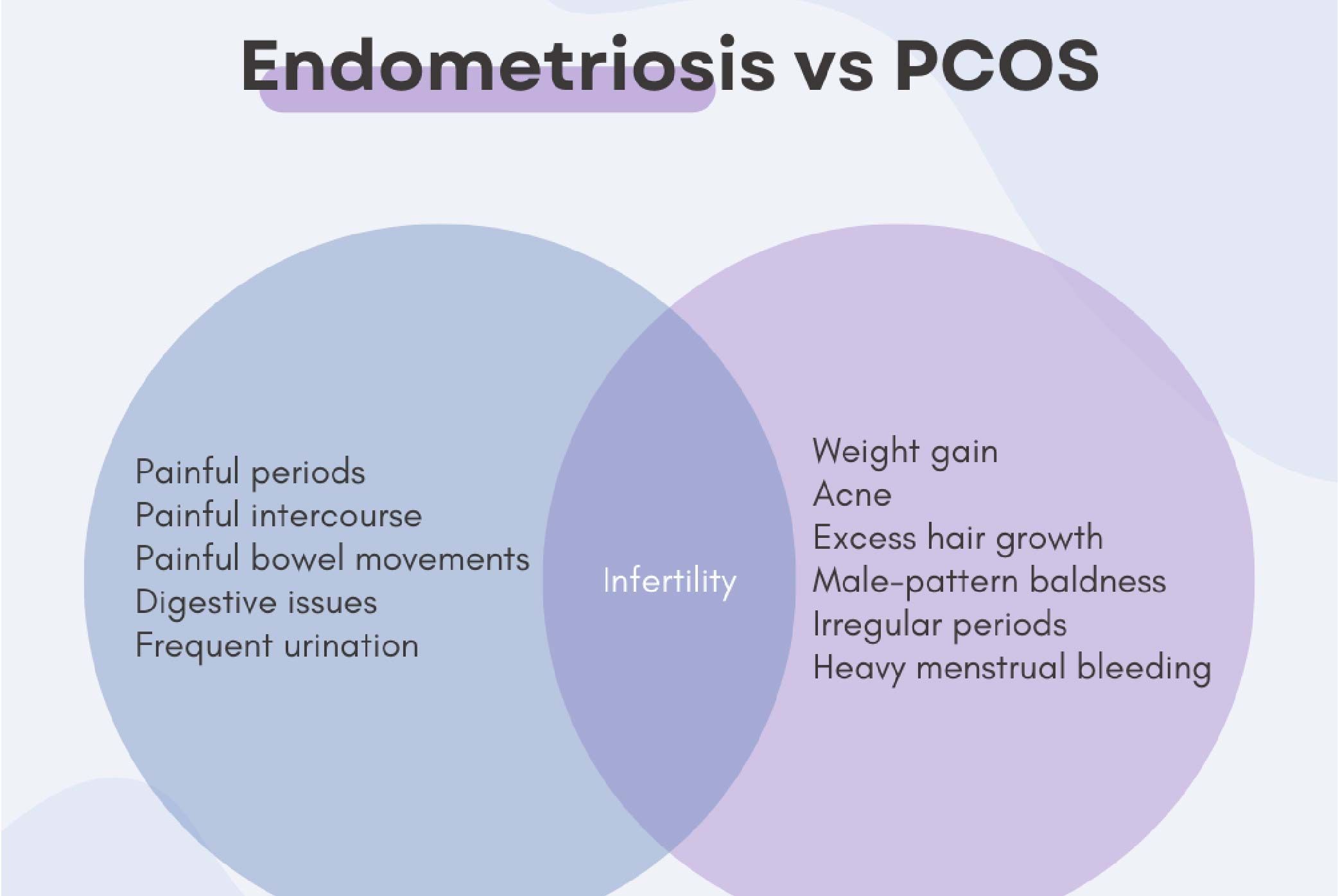









.jpg?updatedAt=1698990658591)



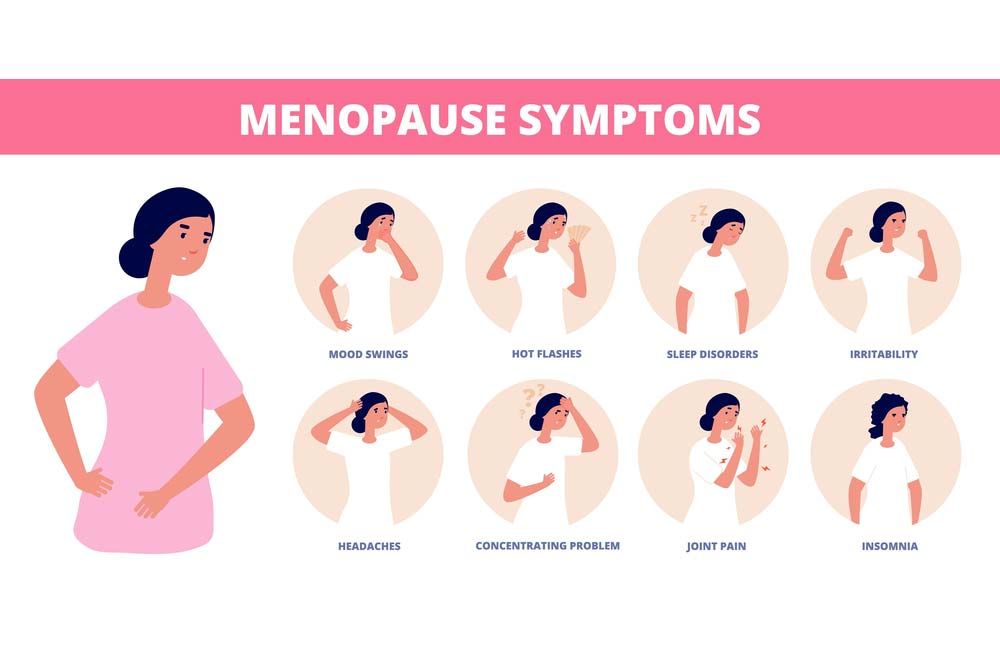




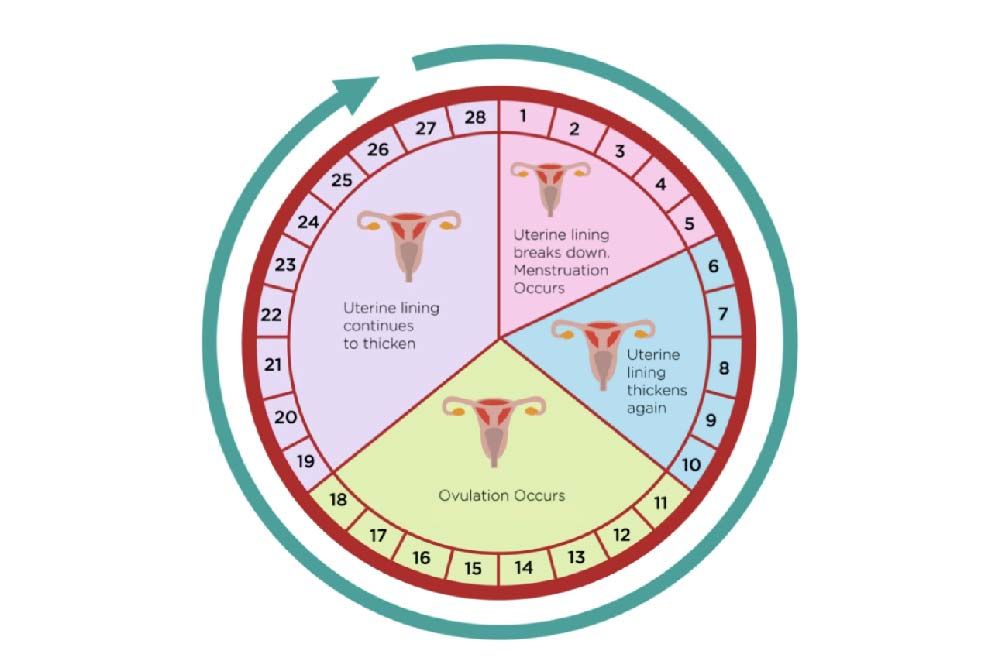


.jpg?updatedAt=1705563681886)
.jpg?updatedAt=1705563778884)

.jpg?updatedAt=1705563897515)
.jpg?updatedAt=1705563967082)
.jpg?updatedAt=1705564021495)

.jpg?updatedAt=1705564129764)
.jpg?updatedAt=1705564238291)











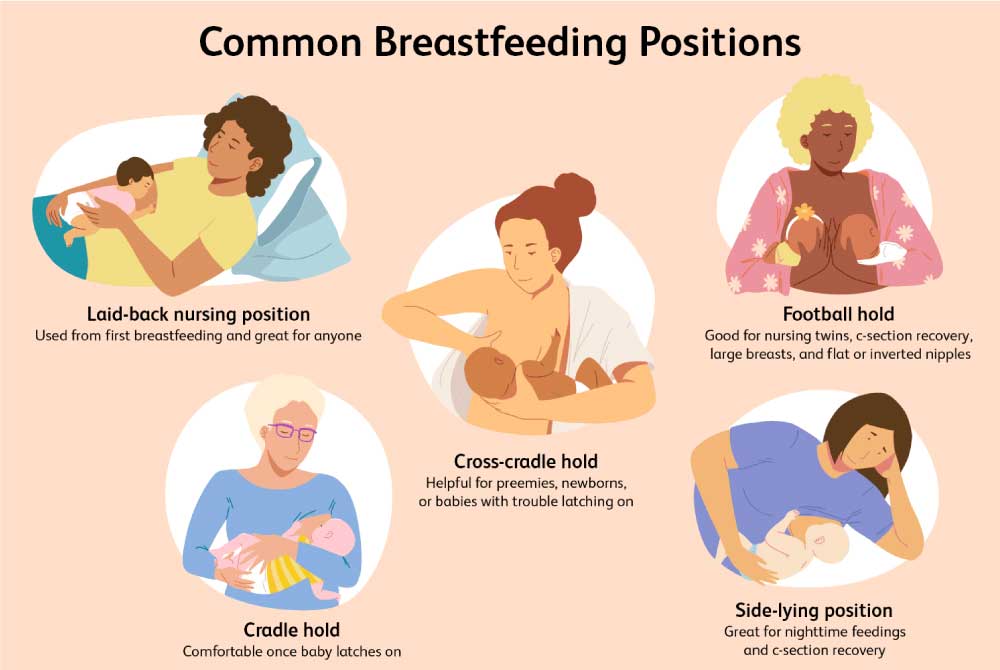






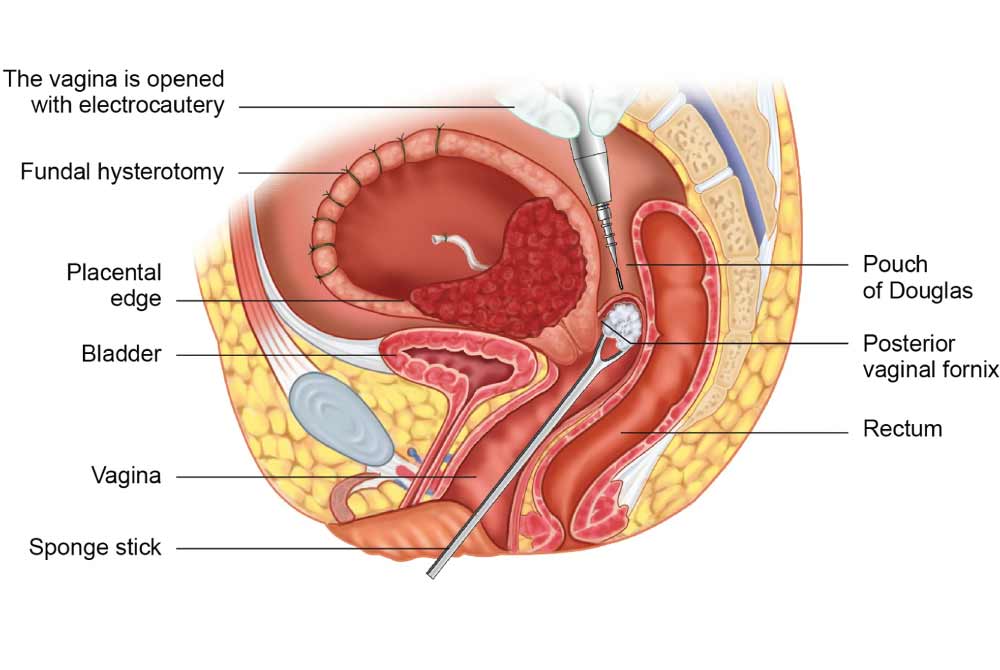





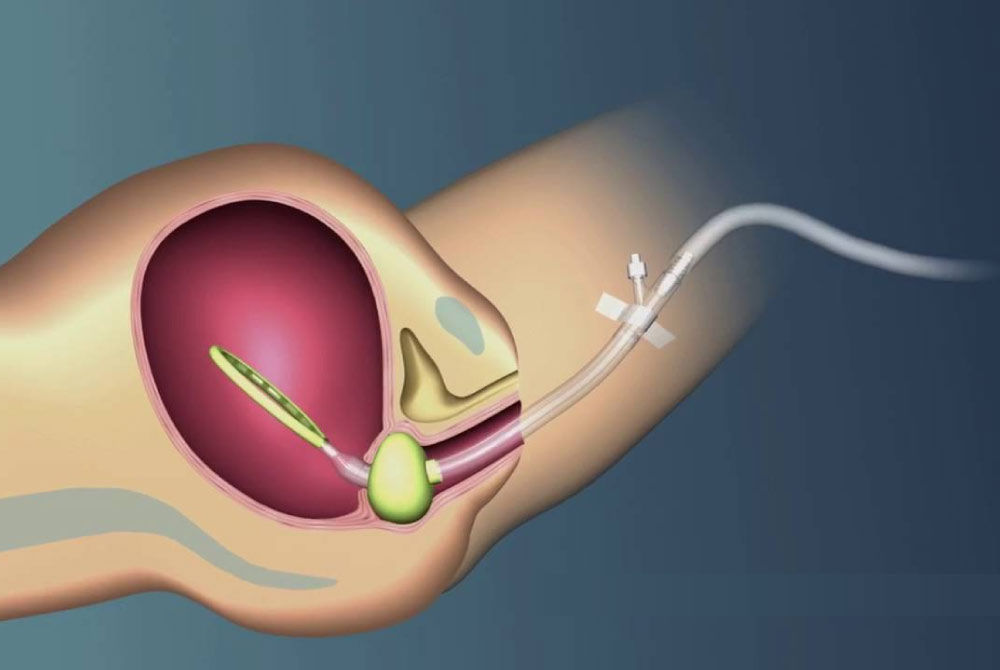
































-as-a-Treatment-Option-for-Female-Infertility.jpg?updatedAt=1710151636366)
-vs.-Paediatric-Intensive-Care-Units-(PICUs)-Understanding-the-Differences.jpg?updatedAt=1710151683178)
.jpg?updatedAt=1710223058371)

.jpg?updatedAt=1712730975677)







_%20A%20Comprehensive%20Guide%20for%20Expectant%20Mothers.jpg?updatedAt=1734505802035)







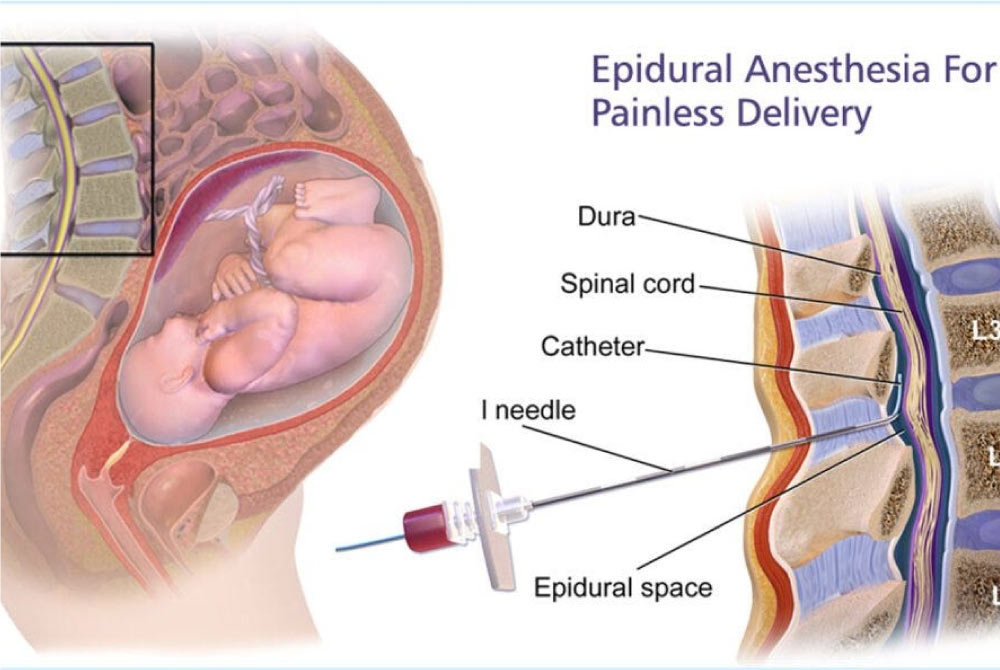
.jpg?updatedAt=1734591693136)





































.jpg?updatedAt=1734591447786)


.jpg?updatedAt=1734591384247)
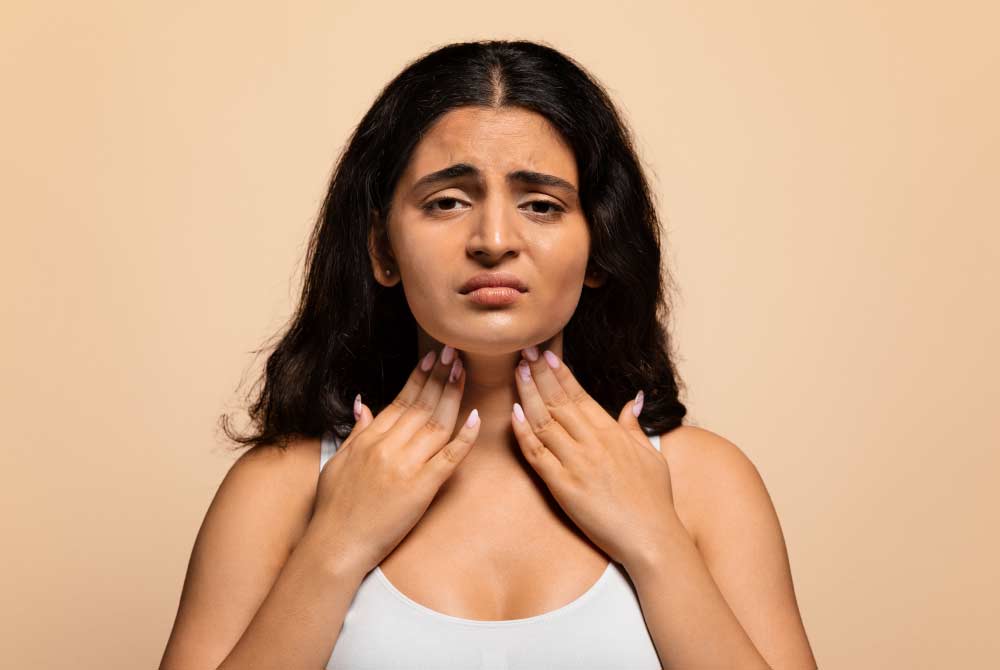



















.jpg?updatedAt=1734591291813)
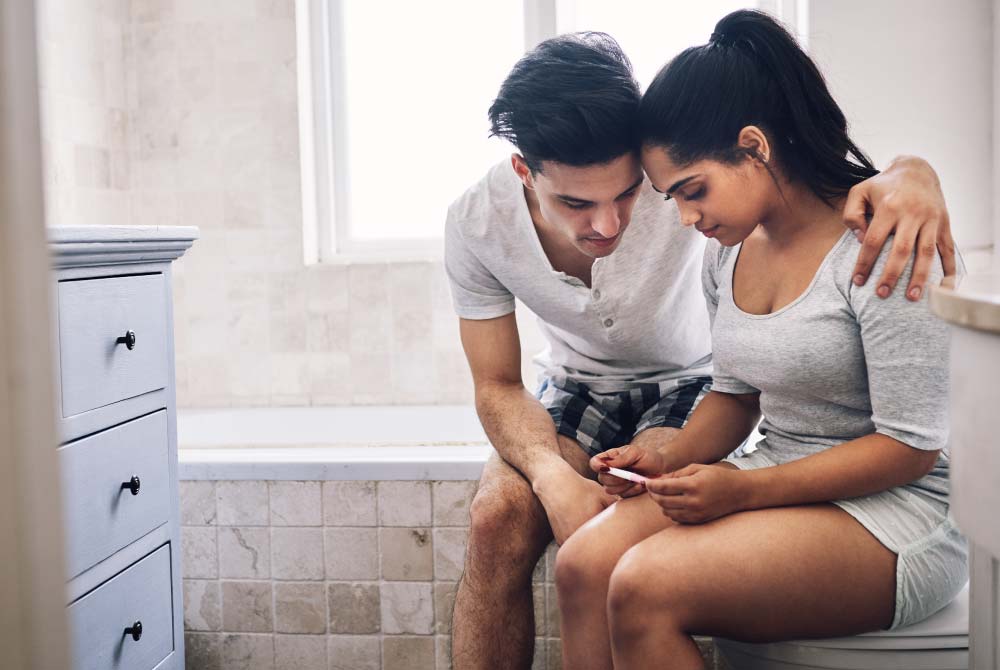
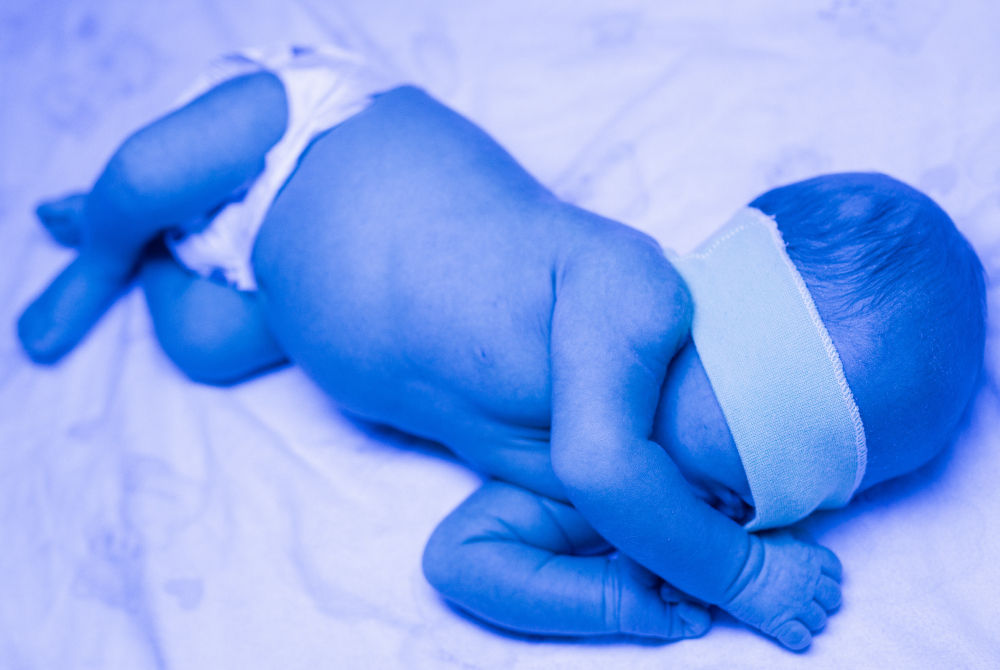
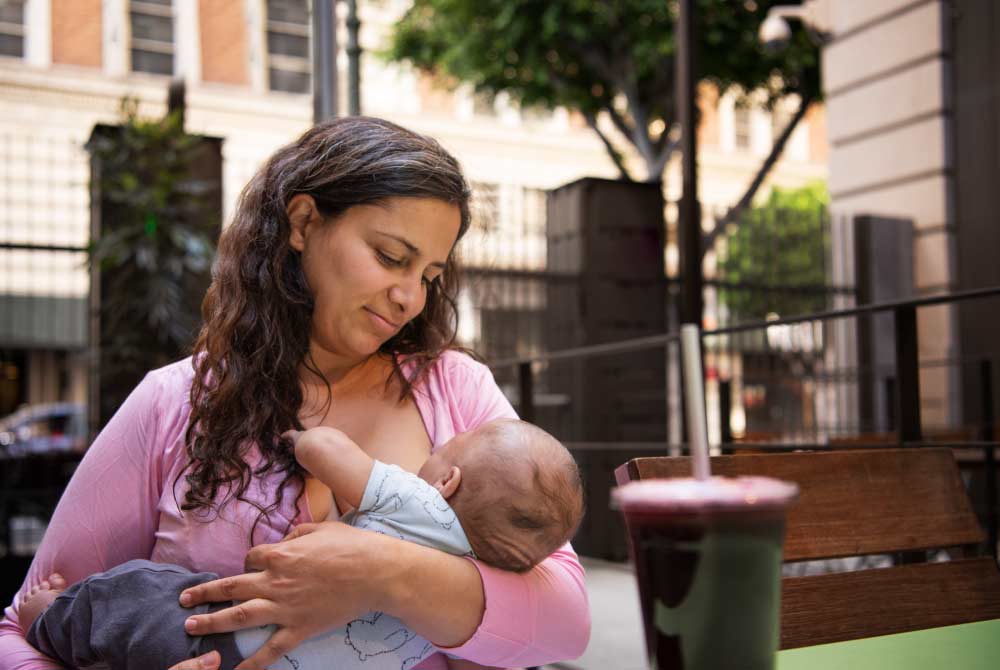









.jpg?updatedAt=1734591024458)




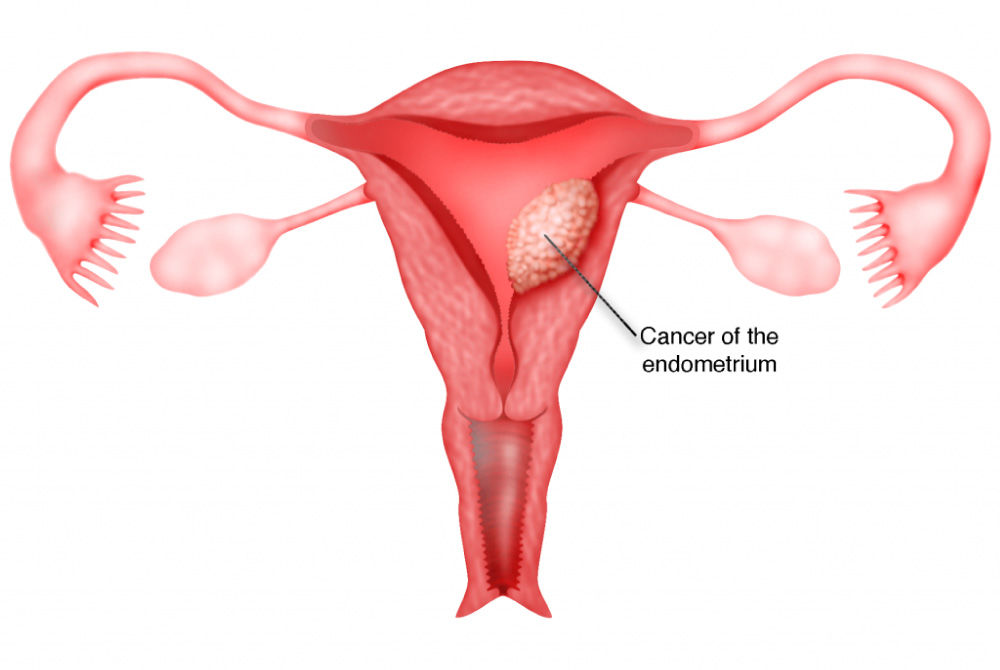


















































.jpg?updatedAt=1736236046716)